
Reasons for Hair Fall in Females
Hair fall is a common concern for many women and can lead to emotional distress and a loss of self-confidence. While it’s normal to lose a small amount of hair each day, excessive shedding may indicate an underlying issue. Hair fall can be influenced by various factors including genetics, hormonal imbalances, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions. Below, we’ll explore these causes in detail and provide insights on how to address them.

1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones play a major role in hair growth and health, and fluctuations can trigger hair fall. Several hormonal conditions can lead to excessive hair shedding in women:
- Pregnancy and Postpartum: Many women experience thick, luscious hair during pregnancy due to increased estrogen levels. However, postpartum hair fall is common as hormone levels stabilize, causing hair that was in the resting phase to shed.
- Menopause: During menopause, estrogen and progesterone levels drop, and androgen levels can rise. This imbalance can result in hair thinning, particularly on the top of the head.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause elevated androgen levels, leading to hair loss, especially in areas where men typically lose hair.
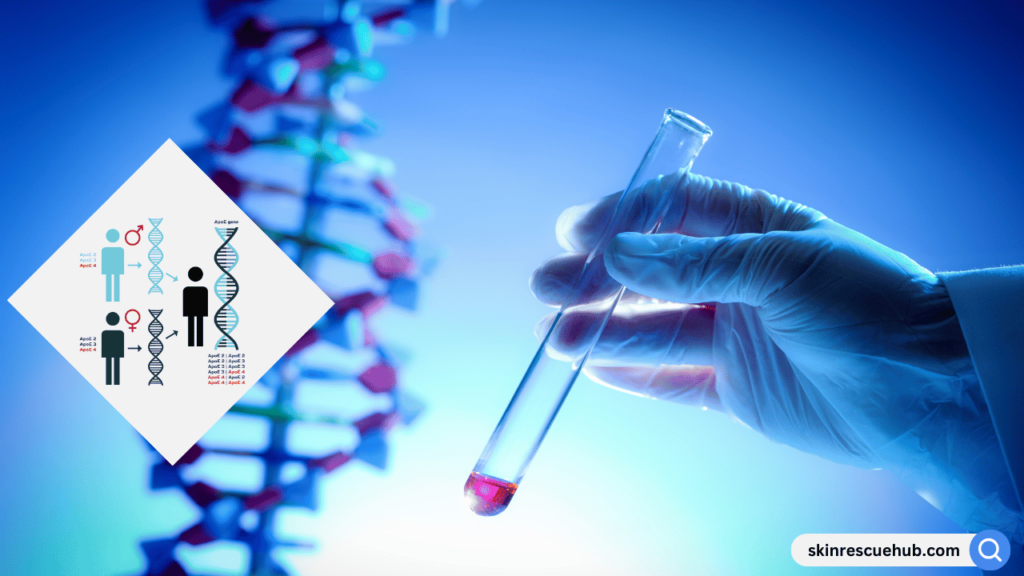

2. Genetic Factors
Hereditary hair loss, known as female-pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, is a genetic condition that affects millions of women. It typically starts with thinning on the crown and may progress gradually. Although it’s more common in postmenopausal women, genetic hair loss can begin as early as in the 20s or 30s.
- Inheritance: This type of hair loss is inherited and is linked to an androgen receptor gene, which makes hair follicles sensitive to hormones.
- Progression: The hair follicles gradually shrink, causing shorter and finer hair, and in some cases, the follicles stop producing hair altogether.
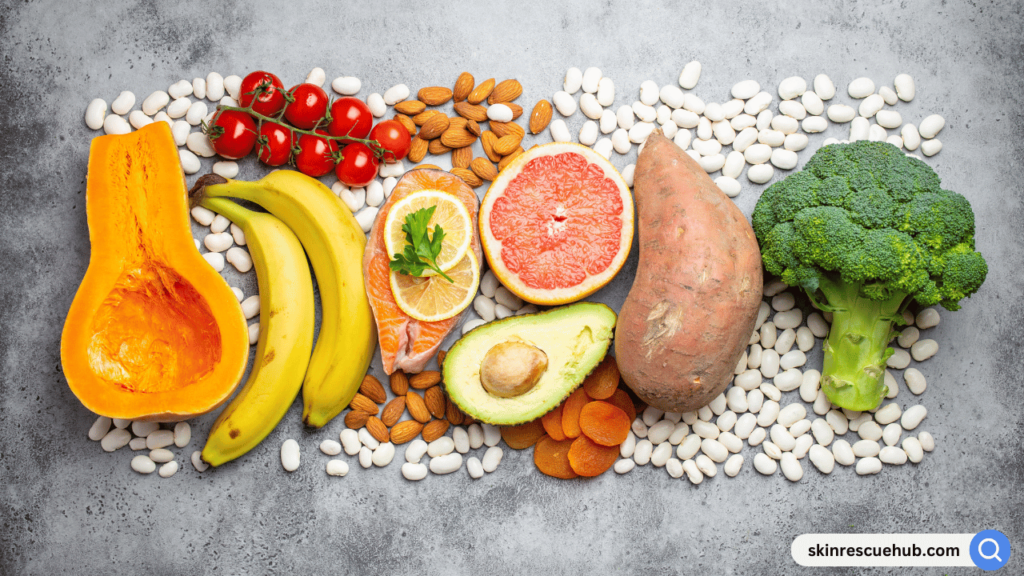

3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Hair requires a variety of nutrients to grow and stay healthy. Deficiencies in these nutrients can weaken hair and lead to shedding:
- Iron Deficiency: Iron plays a crucial role in hair health as it supports red blood cells that carry oxygen to hair follicles. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, which is often associated with hair fall.
- Protein Deficiency: Hair is made primarily of keratin, a type of protein. Insufficient protein intake can weaken hair shafts, leading to breakage.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D is involved in the production of new hair follicles. Low levels of this vitamin can disrupt the hair growth cycle.
- Zinc and Biotin Deficiency: Zinc supports hair tissue growth and repair, while biotin is known to improve hair health. Deficiencies in either nutrient can cause hair thinning.

4. Stress and Anxiety
Physical or emotional stress can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, where a significant amount of hair prematurely enters the resting phase and eventually falls out. Common stress-related triggers include:
- Emotional Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s hormone balance, impacting hair growth. Events like the loss of a loved one, financial difficulties, or relationship issues can induce stress-related hair loss.
- Physical Stress: Physical stress from surgery, illness, or drastic weight loss can also contribute to telogen effluvium, leading to sudden hair shedding.
5. Thyroid Disorders
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, and imbalances in thyroid hormones (either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism) can impact hair growth.
- Hypothyroidism: Low thyroid levels can lead to symptoms like fatigue, dry skin, and hair thinning.
- Hyperthyroidism: High thyroid hormone levels can also cause hair loss, usually along with symptoms like weight loss and irritability.
- Treatment: Thyroid disorders are often treatable with medication, which can help restore hormonal balance and improve hair health.

6. Harsh Hair Treatments and Styling Practices
Excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, and rough handling can damage hair and lead to breakage:
- Heat Styling: Frequent use of hot tools like flat irons, curling irons, and hair dryers can weaken hair, making it more prone to breakage.
- Chemical Treatments: Treatments like hair coloring, perming, and straightening involve harsh chemicals that can damage the hair cuticle, leading to thinning and hair fall.
- Tight Hairstyles: Constantly wearing hair in tight hairstyles (like ponytails or braids) can cause traction alopecia, a condition where hair falls out due to pressure and tension on the follicles.

7. Medications and Medical Treatments
Certain medications and treatments have side effects that include hair loss. These can vary widely in terms of how and why they affect hair growth:
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells, which includes hair cells, often leading to hair loss.
- Birth Control Pills: Some oral contraceptives may cause hair thinning, especially for women who have a family history of hair loss.
- Other Medications: Blood thinners, beta-blockers, and antidepressants are also known to contribute to hair fall.
8. Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune conditions can lead to hair loss when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own hair follicles. Two notable conditions include:
- Alopecia Areata: This condition causes patchy hair loss as the immune system attacks hair follicles.
- Lupus: Lupus can cause diffuse hair loss or hair thinning, sometimes leading to scarring alopecia where hair doesn’t grow back.
9. Scalp Infections and Disorders
An unhealthy scalp can contribute to hair thinning. Conditions like dandruff, psoriasis, and fungal infections can cause scalp inflammation, making it difficult for hair follicles to thrive:
- Fungal Infections: Infections like ringworm can cause hair loss by infecting the scalp and creating areas of hairless patches.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This scalp condition causes red, itchy, flaky skin and is associated with dandruff. In severe cases, it can lead to temporary hair loss.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition causing scalp scales that may damage hair follicles.
10. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including pollution and exposure to toxins, can affect hair health:
- Pollution: Pollutants in the air can settle on the scalp, causing inflammation and damage to hair follicles.
- Sun Exposure: Excessive UV exposure can damage the hair cuticle and cause dryness and breakage.
Addressing Hair Fall in Females
Understanding the root cause of hair fall is essential for determining the most effective treatment. Here are some strategies to combat hair loss and support hair health:
A. Diet and Nutrition
- Incorporate Iron-Rich Foods: Lean meats, beans, and leafy greens can help maintain healthy iron levels.
- Ensure Protein Intake: Eggs, fish, nuts, and dairy are excellent sources of protein for hair strength.
- Include Vitamins and Minerals: A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential vitamins like biotin, zinc, and vitamin D.
B. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Manage Stress: Engage in relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing to reduce stress.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Opt for loose hairstyles to reduce tension on the scalp and avoid pulling on hair.
C. Gentle Hair Care Routine
- Minimize Heat Styling: Allow hair to air dry whenever possible and use heat protectants if you use styling tools.
- Limit Chemical Treatments: Consider semi-permanent dyes and look for gentle products that are less damaging.
- Use a Mild Shampoo: Avoid shampoos with harsh chemicals like sulfates and parabens, as they can strip the hair of natural oils.
D. Medical Consultation and Treatment
- Check for Underlying Conditions: Seek medical advice if you suspect hormonal imbalances, thyroid issues, or nutritional deficiencies.
- Consider Hair Growth Treatments: Options like minoxidil can promote hair growth in certain types of hair loss.
- Explore PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves injecting growth factors into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
E. Over-the-Counter and Natural Remedies
- Minoxidil: Approved by the FDA, minoxidil is an over-the-counter treatment that can slow hair loss and stimulate new hair growth.
- Essential Oils: Oils like rosemary and peppermint may help improve blood circulation to the scalp and stimulate follicles.
F. Scalp Care
Maintaining a healthy scalp can promote hair growth and reduce hair fall. Some suggestions include:
- Regular Exfoliation: Use a gentle scalp scrub once a week to remove buildup and promote blood circulation.
- Moisturizing Treatments: Natural oils like coconut oil and olive oil can provide hydration to the scalp, reducing dryness and flakiness.
When to Seek Professional Help
While it’s normal to experience some degree of hair fall, persistent or excessive shedding should be addressed. Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist (hair specialist) can provide personalized solutions. They can offer diagnostic tests to identify hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, or other underlying causes, and suggest targeted treatments.
Affiliate Disclosure
SkinRescueHub is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
This means that when you purchase products through links on our site, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This commission helps us continue to provide quality content, reviews, and recommendations. Thank you for supporting SkinRescueHub!
Shampoo
Explore our range of exceptional products designed to meet all your needs.

Rs.277

Rs.569
Hair Serum
Explore our range of exceptional products designed to meet all your needs.

Rs.649











