Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably due to DNA damage, often caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Early detection and proper treatment can significantly improve outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the causes, types, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options for skin cancer.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, which usually occurs in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. However, it can also develop in less exposed areas. The three major types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma, each differing in severity and treatment approaches.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Several factors contribute to the development of skin cancer, including:
1. Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to UV rays from the sun and artificial sources like tanning beds damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations.
2. Genetics:
A family history of skin cancer increases the risk, as genetic mutations can make some individuals more susceptible.
3. Fair Skin:
People with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes have less melanin, making them more vulnerable to UV damage.
4. Age:
Older individuals are at a higher risk because of cumulative sun exposure over time.
5. Compromised Immune System:
Those with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients, are at a greater risk.
6. Exposure to Harmful Chemicals:
Prolonged exposure to chemicals like arsenic can contribute to skin cancer development.
Types of Skin Cancer
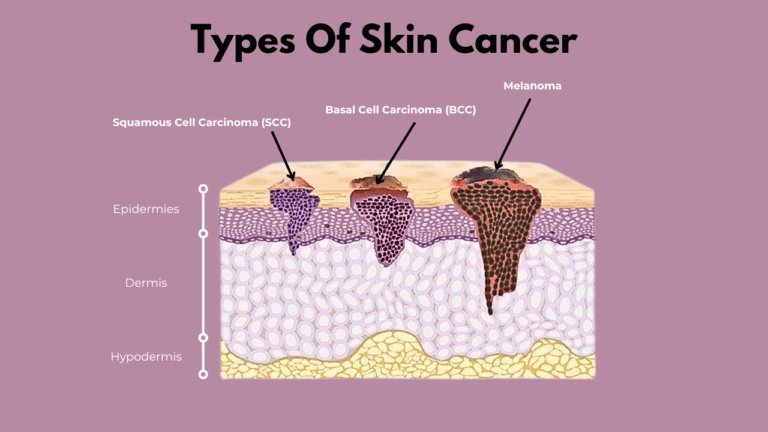
Skin cancer is classified into three primary types based on the affected skin cells:
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Most common but least aggressive form of skin cancer.
Develops in the basal cells, which produce new skin cells.
Commonly found on sun-exposed areas such as the face, ears, and neck.
Symptoms include pearly or waxy bumps, bleeding sores that do not heal, and scaly patches.
Rarely spreads to other parts of the body but can cause local tissue damage.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Second most common type.
Arises in the squamous cells, which make up the middle and outer layers of the skin.
Usually appears on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, and hands.
Symptoms include red, scaly patches, open sores, and growths with a central depression.
Can metastasize if left untreated.
3. Melanoma
Most dangerous form of skin cancer.
Develops in melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin.
Can appear anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun.
Symptoms include asymmetrical moles, irregular borders, varied coloration, and large diameter.
Has a high potential to spread to other organs.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer symptoms vary depending on the type but may include:
New Growths:
Any new or unusual growths on the skin that increase in size.
Changes in Moles:
Alterations in size, shape, or color of existing moles.
Non-Healing Sores:
Sores that do not heal within a few weeks.
Itching or Pain:
Persistent itching, tenderness, or pain in affected areas.
Bleeding or Oozing:
Lesions that bleed or ooze fluid.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Some people have a higher risk of developing skin cancer due to factors such as:
Excessive sun exposure without protection.
A history of severe sunburns.
Having many moles or abnormal moles.
Living at high altitudes or in sunny climates.
Exposure to radiation or harmful chemicals.
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. A dermatologist may perform the following tests:
Skin Examination:
A thorough check of the skin for suspicious growths or changes.
Dermatoscopy:
Using a special magnifying device to examine moles and lesions.
Biopsy:
Removing a sample of the suspicious skin for laboratory analysis.
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer
Treatment depends on the type, size, location, and stage of the cancer. Common treatments include:
1. Surgery
Excisional Surgery: Removing the tumor along with surrounding healthy tissue.
Mohs Surgery: A precise technique that removes layers of cancerous tissue while preserving healthy skin.
2. Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells.
Suitable for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
3. Cryotherapy
Freezing cancerous cells using liquid nitrogen to destroy them.
4. Topical Medications
Creams containing chemotherapy agents or immune-boosting compounds.
5. Chemotherapy
Used for advanced skin cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
6. Immunotherapy
Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells effectively.
7. Photodynamic Therapy
Using light-sensitive drugs and light exposure to kill cancer cells.
Prevention of Skin Cancer
Preventing skin cancer involves adopting protective measures, including:
Using Sunscreen:
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily.
Wearing Protective Clothing:
Cover skin with hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing.
Avoiding Tanning Beds:
Refrain from using artificial tanning devices that emit harmful UV rays.
Seeking Shade:
Stay in the shade, especially during peak sunlight hours (10 AM to 4 PM).
Regular Skin Checks:
Perform self-examinations and visit a dermatologist for annual screenings.
Healthy Diet:
Eating antioxidant-rich foods that promote skin health.
Myths and Facts About Skin Cancer
Myth 1: Only fair-skinned people get skin cancer.
Fact: While fair-skinned individuals are at higher risk, people of all skin tones can develop skin cancer.
Myth 2: Sunscreen is only needed on sunny days.
Fact: UV rays can penetrate clouds and affect skin even on cloudy days.
Myth 3: Skin cancer is not life-threatening.
Fact: Melanoma can be deadly if not diagnosed and treated early.
Living with Skin Cancer
Coping with a skin cancer diagnosis can be challenging. Patients should:
Follow the recommended treatment plan.
Stay informed about their condition.
Seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
Maintain a positive outlook and healthy lifestyle.





