
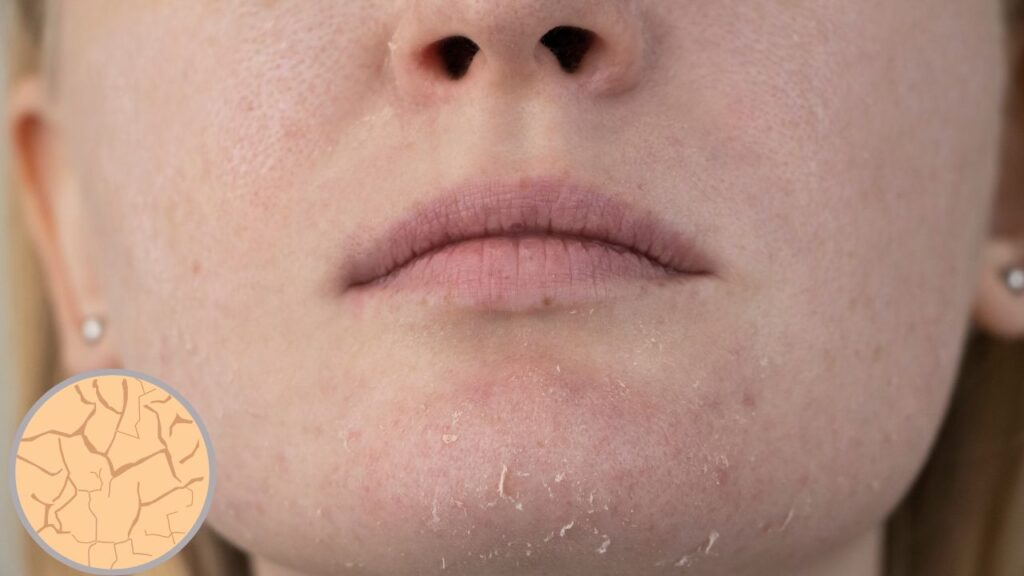
Dry Skin: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions
Dry skin, medically known as xerosis, is a common condition that occurs when the skin lacks the moisture it needs to stay soft and supple. It can affect anyone at any age, though it tends to be more prevalent in older adults. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and solutions is key to managing and preventing dry skin effectively.
Symptoms of Dry Skin
Dry skin can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
Tightness
- The skin feels stretched or uncomfortable, especially after washing.
Flakiness or Peeling
- Small patches of dead skin may peel off, often noticeable on the face, hands, or legs.
Itching (Pruritus)
- Persistent itching can irritate the skin further, sometimes leading to redness or rashes.
Cracks or Fissures
- In severe cases, the skin may develop painful cracks, which can bleed or become infected.
Rough Texture
- The skin feels coarse or uneven to the touch.
Dull Appearance
- Dry skin often lacks the natural glow and appears ashy or pale.
Causes of Dry Skin
Dry skin occurs due to a disruption in the skin’s natural barrier, which results in moisture loss. Several factors contribute to this condition:
Environmental Factors
- Cold Weather: Low humidity during winter strips the skin of its natural oils.
- Hot Showers: Prolonged exposure to hot water can dehydrate the skin.
- Air Conditioning and Heating: Both reduce indoor humidity, leading to dryness.
Genetics
- Some individuals inherit a tendency for dry skin, particularly if they have eczema or other skin conditions.
Aging
- With age, the skin produces less oil and collagen, making it more prone to dryness and thinning.
Skin Care Habits
- Over-washing or using harsh soaps can strip the skin of its natural protective layer.
Medical Conditions
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Causes inflammation and extreme dryness.
- Psoriasis: Leads to dry, scaly patches on the skin.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can reduce skin hydration.
Dehydration
- Not drinking enough water affects the skin’s moisture levels.
Nutritional Deficiencies
- Lack of essential vitamins (A, C, E) and omega-3 fatty acids can exacerbate dryness.
Solutions for Dry Skin
Addressing dry skin involves a combination of lifestyle changes, proper skincare, and sometimes medical intervention. Below are effective strategies to combat dryness:
1. Skincare Routine for Dry Skin
a. Gentle Cleansing
- Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser.
- Avoid soap-based products, which can strip natural oils.
b. Moisturizing
- Apply a moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Choose products with ingredients like:
- Hyaluronic Acid: Attracts and retains moisture.
- Glycerin: A humectant that draws water into the skin.
- Ceramides: Restore the skin’s protective barrier.
c. Exfoliation
- Use a gentle exfoliator once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells.
- Avoid over-exfoliation, which can damage the skin barrier.
d. Sunscreen
- Protect your skin with a broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, even in winter.
2. Home Remedies for Dry Skin
a. Natural Oils
- Coconut oil, olive oil, and almond oil are excellent for moisturizing.
- Apply a thin layer before bed for overnight hydration.
b. Aloe Vera
- Aloe vera gel soothes and hydrates irritated, dry skin.
c. Oatmeal Baths
- Colloidal oatmeal can relieve itching and dryness. Add it to warm bath water for a soothing effect.
d. Honey
- A natural humectant, honey helps to lock in moisture. Apply as a mask and rinse off after 15 minutes.
3. Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Dry Skin
a. Stay Hydrated
- Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and citrus fruits.
b. Avoid Long, Hot Showers
- Opt for lukewarm water when bathing.
- Limit showers to 10-15 minutes.
c. Use a Humidifier
- A humidifier adds moisture to indoor air, preventing your skin from drying out.
d. Wear Protective Clothing
- During winter, cover your skin with gloves and scarves to shield it from cold winds.
4. Nutritional Tips for Healthy Skin
a. Include Skin-Boosting Nutrients
- Vitamin E: Found in nuts, seeds, and spinach, it nourishes the skin.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Present in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, they help maintain the skin’s elasticity.
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits and bell peppers promote collagen production.
b. Avoid Skin-Damaging Foods
- Minimize processed and sugary foods, which can dehydrate the skin.
5. When to See a Dermatologist
If dry skin persists despite home remedies and proper skincare, consult a dermatologist. Professional treatment may include:
- Prescription Moisturizers: For severe cases of dryness.
- Topical Steroids: To manage inflammation and itching.
- Phototherapy: Light-based treatments for chronic conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
Common Myths About Dry Skin
Myth: Drinking water alone can cure dry skin.
- Truth: While hydration is important, external skincare is equally vital.
Myth: Oily skin doesn’t get dry.
- Truth: Even oily skin can experience surface dehydration.
Myth: You don’t need moisturizer if your skin feels oily.
- Truth: Using a lightweight, hydrating moisturizer is essential for all skin types.
